James Reid, Sandra Kachhia, Paul Dougall, John Shovelton, Duarte Molha, Christina Taylor, Jagath Kasturiarachchi, Jolyon Holdstock, Venu Pullabhatla, Laura Parkes, Ewa Marek, Natalie Milner, Emma Shipstone, Douglas Hurd
The detection of Copy Number Variants (CNVs) in intellectual disability and developmental delay (ID/DD) samples is crucial in elucidating the genetic cause of abnormality. We have developed a targeted NGS panel and analytical software (Interpret) to accurately detect CNVs, as well as SNVs, indels and LOH.
The assay uses a bait capture approach, which is able to capture the exons and untranslated regions (UTRs) from over 700 genes, chosen for their relevance in ID/DD, as well as a range of backbone regions across the genome. Combined with OGTs proprietary CNV detection algorithm in the software, both intragenic and large ‘backbone’ CNVs can be detected robustly.
We implemented a web-based solution that runs OGTs NGS analysis pipeline, comprising many state-of-the-art open-source NGS software tools. These tools were carefully chosen and deployed using containers to ensure cross-platform compatibility and reproducibility. Pipeline optimisation and performance was assessed using equivalent array data and reference materials.
We will outline the results from over 200 intellectual disability and developmental delay research samples to demonstrate the efficiency of the CNV, SNV and LOH detection. The study demonstrated that the assay automatically called 100% of SNVs and 97% of reported pathogenic CNVs (including small intragenic CNVs), the uncalled CNVs were visible on Interpret but the protocol of the study precluded them from being called. We have described an improved method to investigate ID/DD samples, providing critical information on not just CNVs, but SNVs and Indels as well.
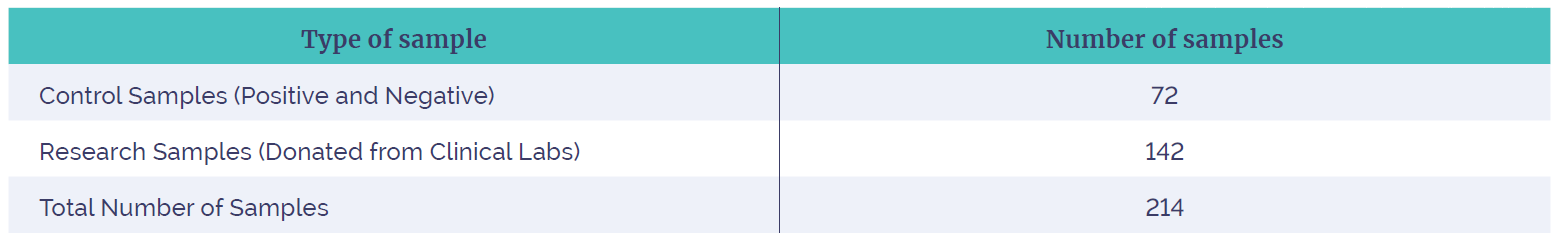
Table 1: The types of samples used in the study to test the reagents and software. These were designed to test all aspects of the system namely, the SNV / Indel, CNV (large and small) and LOH performance. The samples included control and research samples from genetic laboratories, where a pathogenic CNV, SNV, Indel or stretch of LOH had been identified. These were identified by microarrays (CNVs, LOH) or sequencing (SNV, Indel).

A small number of mosaic samples with CNVs were included. The detection of these is dependent on the size of the aberration and the level of mosaicism. Our criteria for including mosaic calls was that the aberration be >5Mb in size and a mosaicism of 50% or more.
This study, using a large range of clinical research samples, demonstrates that CytoSure™ Constitutional NGS solution is able to detect pathogenic CNVs and LOH with a performance on par with microarrays – as demonstrated in the Results I section. These can be large CNVs (Figure 5), megabases in size, or small intragenic CNVs (Figure 6). We also called 100% of reported pathogenic SNVs/Indels, showing the precision and sensitivity of the assay. In the Results II section we discussed the ability of the assay to detect CNVs in low percentage mosaic samples, a result of the bait design and accuracy of Interpret software.
CytoSure Constitutional NGS’ ability to call both SNVs and CNVs gives this assay a larger scope in calling genetic aberrations than in microarrays alone.
CytoSure®: For Research Use Only; Not for Diagnostic Procedures.
Call +44 (0)1865 856800 Email contact@ogt.com
Send us a message and we will get back to you