Jacqueline Chan, Sabine Eckert, Lyudmila Georgieva and Graham Speight (OGT, Begbroke Science Park, Begbroke Hill, Woodstock Road, Begbroke, Oxford, UK)
One of the challenges in cancer research is the high level of genetic complexity and tumour heterogeneity.
Research that generates detailed information about the genetic profile of each individual tumour will further our understanding and may be used in the future to guide treatment strategies1 .
NGS has enabled the simultaneous study of multiple mutations in high-penetrance cancer predisposition genes. However, tissue biopsies are typically archived as formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) blocks which can significantly compromise the quality and amount of nucleic acids available for genomics research.
To overcome these issues, we have used the SureSeq™ FFPE DNA Repair Mix, in combination with a hybridisation-based NGS custom enrichment panel, the SureSeq Ovarian Cancer Panel (Table 1) to identify somatic variation in key DNA repair genes associated with ovarian cancer.
To evaluate the application of a hybridisation-based approach we:
The SureSeq hybridisation-based enrichment was used throughout this study; the workflow of this is outlined below in Figure 1.
We tested a range of FFPE-derived DNA and formalin compromised DNA (Horizon Diagnostics - HD803 and HD799) and found pre-treatment with the SureSeq FFPE DNA Repair Mix significantly improves the number of on-target reads, thereby increasing the flexibility of the assay (Figure 2A). Use of the Repair mix also enables a reduced DNA input down to 50 ng to be used (if necessary) whilst maintaining a good depth of coverage (Figure 2B).
To confidently call low frequency variants, NGS reads need to be evenly distributed across all regions of interest. Uniformity of coverage is a useful value with which to compare this distribution and can be expressed as the percentage of target bases that have >20% of the mean coverage.
As reported extensively in the literature1-3, we found the uniformity of coverage from hybridisation-based capture approaches, such as SureSeq, consistently outperform those enriched using amplicon-based methods (Figure 3). The uniformity of coverage for most samples is >99% of bases covered at >20% of the mean, ensuring that all bases within the panel can be assessed confidently. In addition, the use of hybridisation-based capture instead of amplification-based enrichment allows the removal of PCR duplicates which can obscure the minor alleles present within a sample.
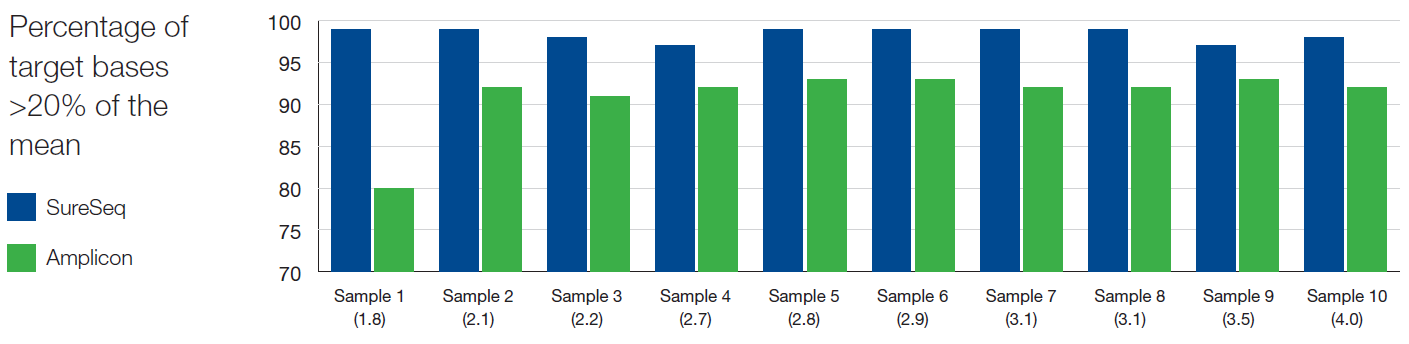
Figure 3: Assessment of the uniformity of sequencing coverage from FFPE-derived DNA using an amplicon and the SureSeq hybridisation-based capture approaches. Enrichment by SureSeq (dark blue bars) demonstrates better uniformity than that of an amplicon-based approach (green bars). Samples are ordered by increasing DIN determined by Agilent 2200 TapeStation – value in brackets.

We tested over 100 EOC samples determined by pathology to contain ≥40% tumour cells and identified one or more deleterious TP53 variant(s) with the minor allele frequencies (MAF) ranging from 1 to 87%. In addition to the mutations in TP53, some samples were found to have variants in BRCA1 (Figure 5). Figures 4 – 5 were visualised using Integrated Genomics Viewer4 ; the grey vertical bars denote the depth of coverage per base, green horizontal bars the targeted region, and the red heatmap - the GC content.
SureSeq: For Research Use Only; Not for Diagnostic Procedures.
Samples kindly provided by –
Call +44 (0)1865 856800 Email contact@ogt.com
Send us a message and we will get back to you